Pumps are essential machines in various industries, serving crucial roles in transporting fluids.
With a wide range of types and designs available, choosing the right pump for specific applications is vital.
Among the most common types are submersible and non-submersible pumps. Understanding the distinctions between these two categories will empower you to make informed decisions tailored to your operational needs.
What are Submersible Pumps?
Definition of Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps are engineered for operation while fully immersed in the fluid they are designed to pump.
This unique design features a sealed motor that prevents water entry, safeguarding the motor from potential damage.
The construction of submersible pumps allows them to efficiently handle various fluids in challenging environments.
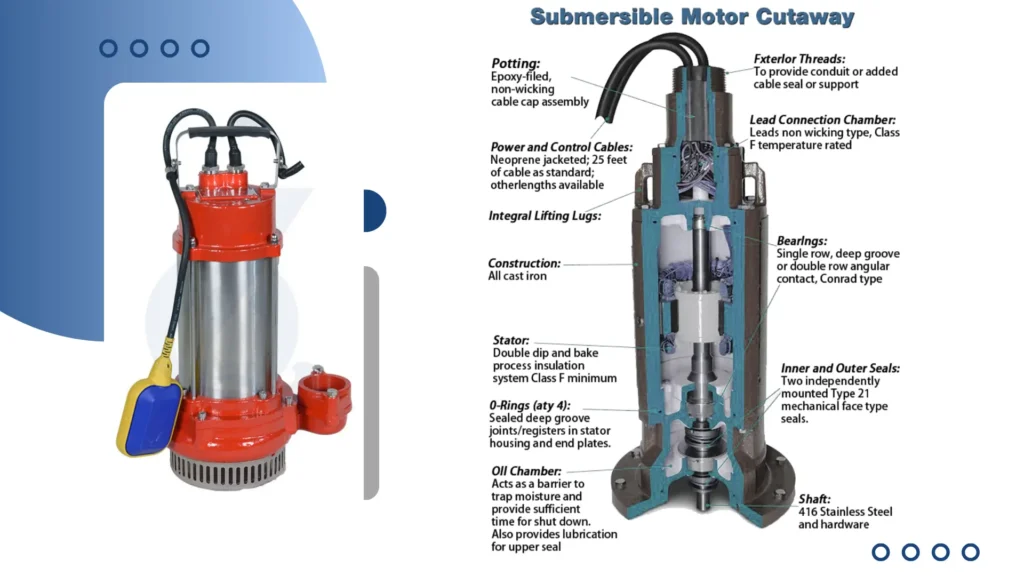
How Do Submersible Pumps Work?
The operation of submersible pumps involves a motor positioned at the pump’s bottom, which drives an impeller. This impeller plays a crucial role in moving the fluid, as it forces the liquid upward through a discharge pipe.
The submerged design enhances efficiency, particularly in deep-water applications, since gravity aids in fluid movement, reducing energy consumption.
Common Applications of Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps find extensive use across various sectors. They are particularly effective for groundwater extraction, where they can efficiently draw water from deep wells.
These pumps are essential in sewage pumping, as their design allows them to handle wastewater with solids.
In construction, submersible pumps are frequently employed for dewatering tasks, ensuring work sites remain dry and safe.
Advantages of Submersible Pumps
One of the primary advantages of submersible pumps is their high efficiency, as they eliminate the need for priming, which can be a cumbersome process with other pump types.
Their quiet operation is another benefit, making them suitable for residential areas or environments where noise reduction is a priority.
Furthermore, submersible pumps are capable of managing solids within the fluid, adding to their versatility for various applications.
And More:
What is a Submersible Pump in Construction?
What are Non-Submersible Pumps?
Definition of Non-Submersible Pumps
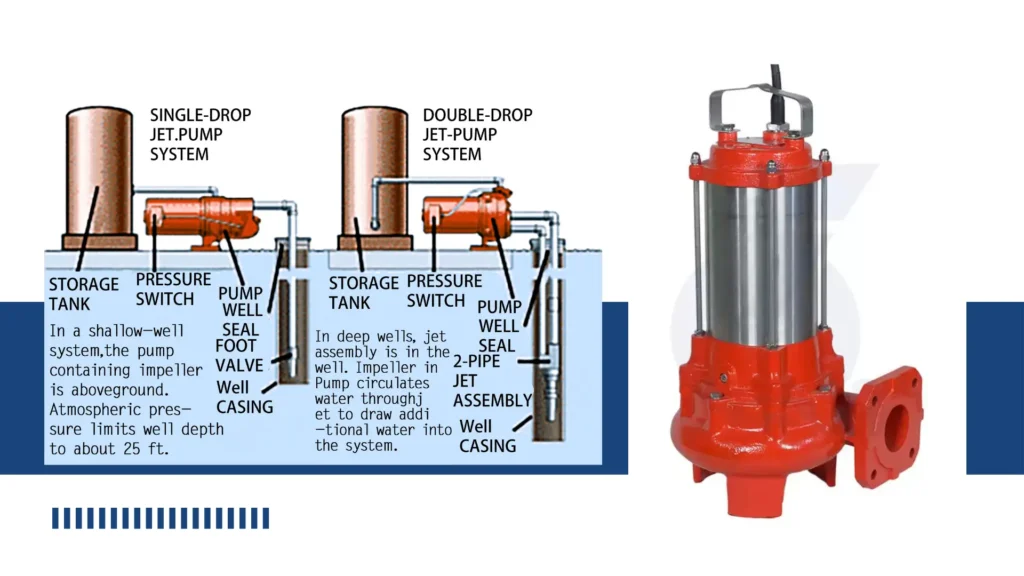
Non-submersible pumps, commonly referred to as surface pumps, are designed to be installed above the fluid level they are pumping. This positioning allows them to rely on suction to draw the fluid into the pump.
This design is prevalent in scenarios where the fluid source is accessible, enabling efficient operation without the complexities associated with submerged systems.
How Do Non-Submersible Pumps Work?
These pumps operate with a motor situated above the fluid level, which creates a vacuum effect. This vacuum pulls the fluid into the pump, where it is then propelled through a discharge pipe.
The reliance on suction means that non-submersible pumps are typically used in applications where the fluid does not need to be lifted from significant depths.
Common Applications of Non-Submersible Pumps
Non-submersible pumps are widely utilized in various applications, including irrigation systems, where they help deliver water to crops efficiently.
They are also commonly employed in drainage systems to remove excess water and prevent flooding.
These pumps are frequently used in municipal water supply systems, ensuring that clean water is delivered reliably to communities.
Advantages of Non-Submersible Pumps
A significant advantage of non-submersible pumps is their ease of maintenance. Positioned above ground, these pumps are more accessible for servicing and repairs, which can lead to reduced downtime.
Moreover, their design often results in a longer lifespan in certain applications, as they experience less exposure to potentially corrosive fluids compared to submersible pumps.
How Do Submersible and Non-Submersible Pumps Compare?
Efficiency Differences
Submersible pumps are generally recognized for their superior efficiency, particularly in deep applications.
Their design allows them to operate effectively underwater, utilizing the natural pressure of the fluid to enhance performance.
Non-submersible pumps often face limitations due to their reliance on suction.
This can lead to decreased efficiency when pumping from depths, as the suction must overcome gravitational forces, potentially resulting in insufficient fluid flow.
Cost Considerations
When examining cost considerations, submersible pumps typically come with higher upfront expenses.
This is largely due to their specialized design and the materials used to ensure they are waterproof. However, the initial investment can pay off over time; their efficiency can lead to lower energy costs and reduced operational expenses.
On the other hand, non-submersible pumps usually have lower initial costs, making them more attractive for short-term projects or budget-conscious applications.
The trade-off may involve higher operational costs in the long run, especially if they are less efficient.

Maintenance Needs
Maintenance needs vary significantly between the two pump types. Submersible pumps require diligent upkeep to prevent water from damaging the motor.
Regular inspections and maintenance routines are essential to ensure the seals remain intact and the pump operates smoothly.
Non-submersible pumps are easier to service due to their above-ground placement. Accessibility simplifies the maintenance process, allowing for quicker repairs and less downtime, which can be a critical factor for ongoing operations.
Lifespan and Durability
The lifespan and durability of both submersible and non-submersible pumps can differ based on several factors, including usage patterns and maintenance practices.
Submersible pumps may experience increased wear due to their constant immersion in fluids, which can expose them to contaminants and corrosive substances. In contrast, non-submersible pumps can potentially enjoy a longer lifespan if they are maintained properly and protected from harsh environmental conditions.
The choice between the two should consider the specific operational context and maintenance capabilities.
Also Read:
- The Best Type of Submersible Pump Depends on Specific Needs
- Comparison Between Steel and Cast Iron Submersible Pumps
Which Pump is Right for Your Needs?
Assessing Your Application
When determining the appropriate pump for your needs, it’s crucial to assess the specific requirements of your project.
This includes evaluating the depth of the water source, as submersible pumps excel in deep-well applications, while non-submersible pumps are better suited for shallower sources.
Additionally, consider the type of fluid being pumped; some fluids may pose challenges that favor one pump type over the other.
Budget Considerations
Budget considerations play a significant role in the decision-making process.
Evaluating your budget should encompass not only the initial investment for the pump but also the long-term operational costs.
Submersible pumps may have a higher upfront cost, but their efficiency could lead to savings over time. Non-submersible pumps may be more affordable initially, but ongoing costs, including energy consumption and potential maintenance, should also be factored into the overall budget analysis.

Maintenance Capability
Your ability to perform maintenance on the pump is another important consideration. If accessibility is a challenge in your environment, a non-submersible pump may be more suitable, as it simplifies maintenance tasks.
On the other hand, if you have the resources and capability to conduct regular maintenance on a submersible pump, its efficiency and performance benefits might outweigh the challenges.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can significantly influence pump performance and longevity. Submersible pumps are often better suited for wet conditions and environments where flooding may occur, as they are designed to operate underwater.
Conversely, non-submersible pumps are ideal for drier areas where water is readily accessible and less prone to contamination.
Assessing the environmental conditions of your project site will help determine which pump type will perform best.
What Are the Key Takeaways?
Summary of Key Differences
Submersible pumps excel in deep applications, operating efficiently while fully submerged in the fluid they are pumping.
Their design allows them to leverage the surrounding pressure, making them ideal for tasks like groundwater extraction and sewage pumping.
In contrast, non-submersible pumps, also known as surface pumps, are installed above the fluid level, making them easier to maintain and service.
This above-ground positioning is particularly advantageous for applications where the fluid source is easily accessible, such as irrigation or drainage systems.
Importance of Choosing the Right Pump
Selecting the right pump is critical as it directly affects efficiency, operational costs, and maintenance requirements.
An informed choice can lead to significant savings in energy and repairs over time.
Understanding your specific needs—such as the depth of the water source, the type of fluid being pumped, and your budget—will help ensure that you choose a pump that aligns with your operational goals.
The right pump not only enhances productivity but also contributes to the longevity of your investment.

Future Considerations
Awareness of advancements in pump technology is essential for making informed decisions in the future.
Innovations in design and materials can lead to more efficient models that offer improved performance and reduced energy consumption.
Staying updated on these developments can help you adopt newer models that may provide enhanced features, such as automated monitoring systems or better corrosion resistance.
Embracing technology will ensure that your pumping solutions remain effective and cost-efficient.
Conclusion
Grasping the differences between submersible and non-submersible pumps is vital for making an informed purchasing decision.
A thorough understanding of your application, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities will guide you in selecting the most suitable pump for your needs.
Taking the time to evaluate these factors will ultimately lead to a more efficient and reliable pumping solution, ensuring that your operations run smoothly and effectively.

