Submersible pumps balance the use of water resources by efficiently moving fluids for public health and environmental protection.
Their reliability is most desired in urban areas where population density heightens the demand for these systems of managing water.
This blog post highlights various applications and benefits of industrial submersible pumps.
In this accessible overview, we want to give potential buyers the knowledge they need to make smart decisions regarding their water and wastewater management solutions.
When valued, resource management will be better, and investing in the use of technology will offer efficiency gains and increase sustainability.
Learn More:
- The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Submersible Pumps
- What is a Submersible Pump Used For?
- Industrial and Commercial Submersible Pumps
Municipal and Industrial Water Supply
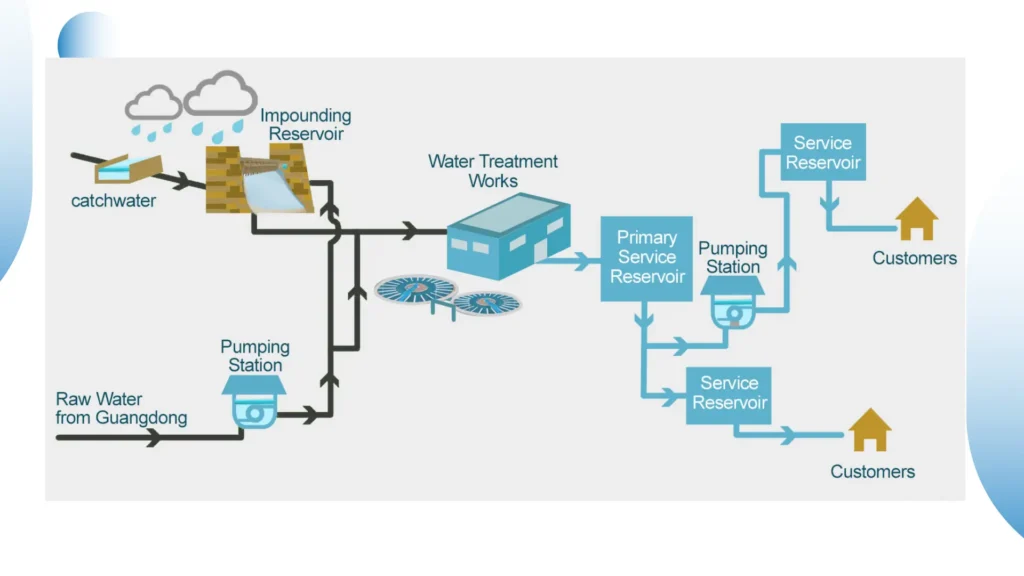
Role of Submersible Pumps in Municipal Water Systems
In the municipalities’ water supply systems, submersible pumps play a huge role in the supply of large volumes of water from the aquifers to the treatment facilities.
The design of the pumps is basically to handle the volume of water effectively in order to ensure a continuous supply of clean drinking water to the communities.
This makes them reliable, even in municipal applications, for operation under harsh conditions, such as very deep wells.
Industrial Applications
Submersible pumps find their application in industries for several purposes: the supply of cooling water, stormwater management, and filtration systems.
These are common in manufacturing plants, electrical generating plants, and food processing plants where water flow control is vital in sustaining process efficiency.
By this means, industries can maintain productivity while effectively regulating their water supplies.
Advantages of Submersible Pumps in Water Supply
Advantages of submersible pumps in water supply systems are that, due to their design, they save many erection works of pipes and reduce the installation cost and time.
Secondly, without noise, efficiency at work reduces disturbances in populated areas.
Lastly, the capacity to pump substantial flow rates at Radical heads maintains energy efficiency and means lower costs during operation; therefore, these pumps are very appealing to municipalities and industries alike.
Drainage and Sewage Management
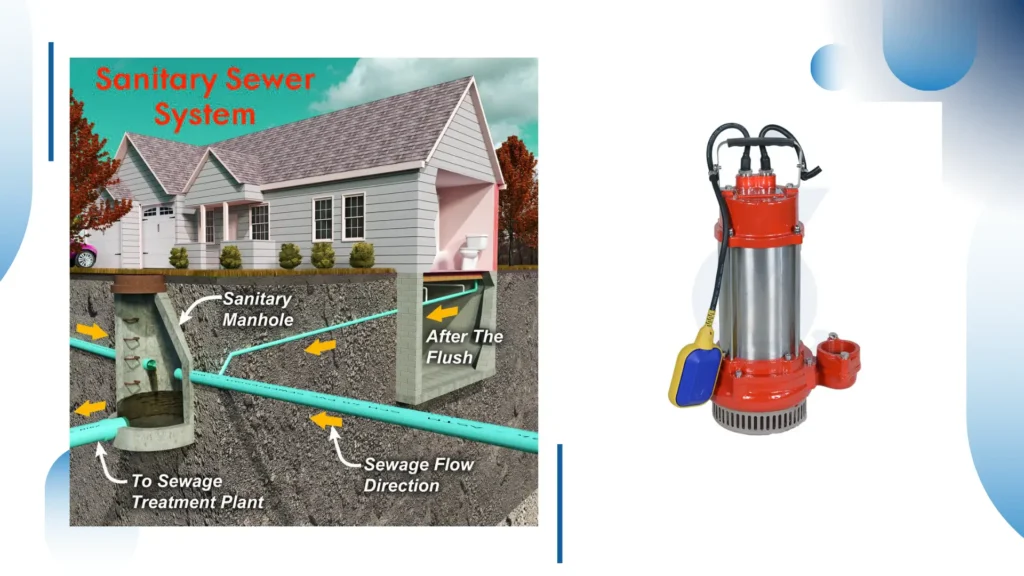
Sewage Systems
It forms a very significant part in sewage systems, as it is installed at lift stations and sewage treatment facilities.
These noisemakers do an efficient job of transferring wastewater from the low to high elevations to ensure that the water reaches the treatment plants with no delays.
Because it operates while submerged, it has direct access to the fluid, enhancing the efficiency and reliability of pumping.
Importance in Flooding Prevention and Wastewater Management
It is the backbone of preventing flooding, especially in cities which are bounded to experience heavy rainfall.
Submersible pumps govern the extra water amount during storms, minimizing overflow and risks of contamination.
They have been very instrumental in ensuring that wastewater reaches the treatment plants as soon as possible for the sake of public health and the integrity of the environment.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
Countless cities have installed submersible pumps in their sewage and found this very effective.
For example, a metropolitan city by installing submersible pumps into its sewage was able to cut the overflows by over 30%.
Case studies like these point toward dependability and effectiveness in the working of such pumps relating to urban wastewater handling issues and, as such, act as inspirers for other cities with respect to how to act.
Irrigation and Agriculture Uses
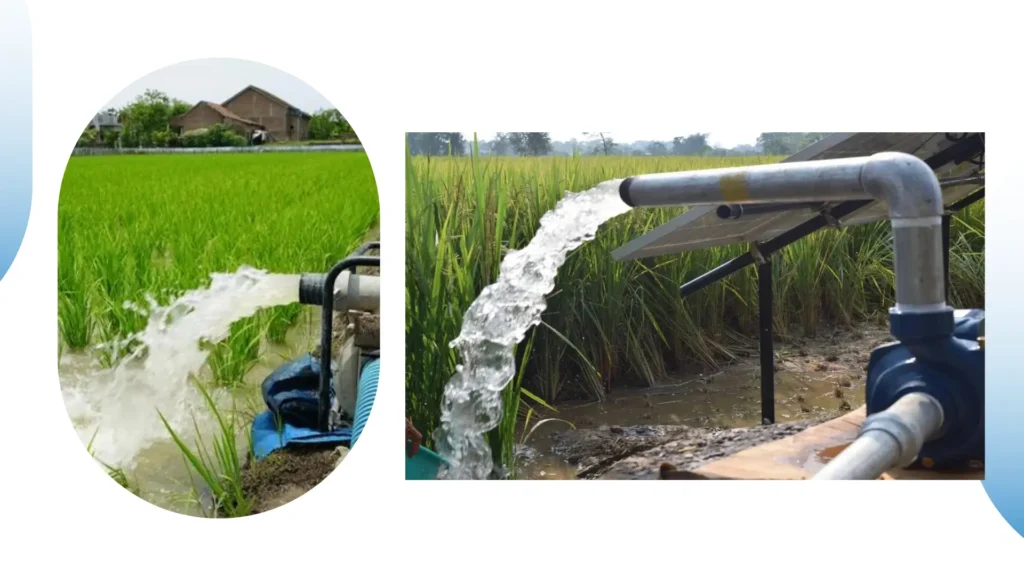
Role of Submersible Pumps in Agriculture
Agricultural applications include irrigation systems in which the submerged pump would be used to supply water to crops.
They are very helpful in areas where surface water is scarce because farmers can obtain the water from beneath the surface.
The ability to operate from nearly any depth within reason makes them suitable for nearly all agricultural situations.
Efficiency and Effectiveness in Water Distribution
The submersible pumps disperse water evenly over big farm expanses. This efficiency in dispersion minimizes water waste, hence allowing farmers to optimize their water usage in irrigation.
As a result of this consistency in water supply, the pumps allow farmers to keep crops healthy and raise productivity.
Impact on Crop Yield and Sustainability
Directly, the use of submersible pumps in irrigation improves crop yield.
Farmers can achieve a higher production by regular and proper watering while at the same time achieving sustainable farming.
This responsible utilization of the groundwater resource promotes long-term agricultural sustainability that results in food security.

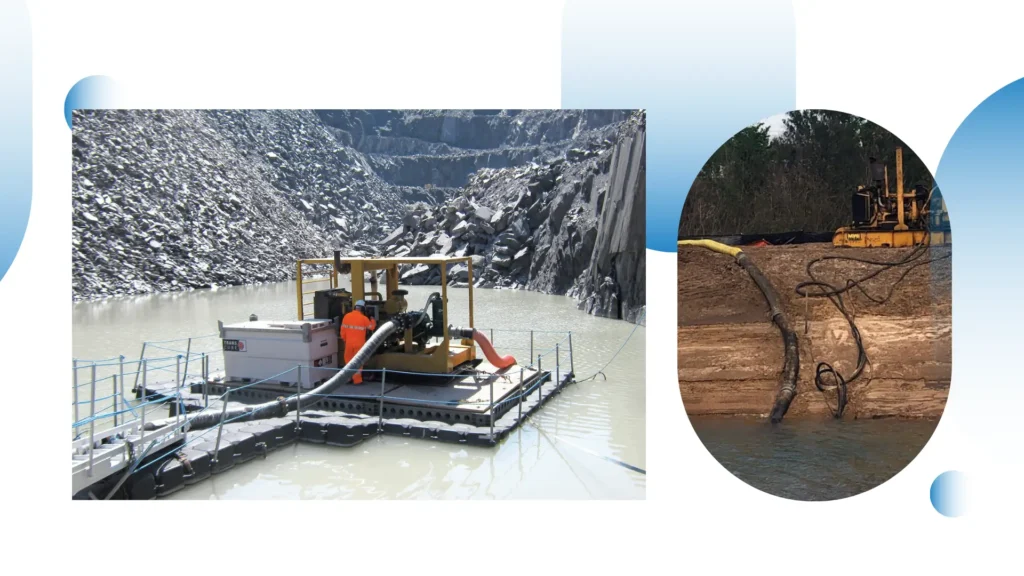
Dewatering in Construction and Mining
Dewatering Necessity in Construction Sites
Dewatering is one of the necessary works associated with any kind of construction process, as often construction needs to be performed on land that contains a high level of water just beneath its surface.
Thus, submersible pumps are utilized for removing additional water from the excavation site in order to keep it dry and safe during the construction period.
This becomes one of the most important roles in ensuring that structural integrity is not compromised, besides preventing delays caused in construction by any reason of accumulation of water.
Submersible Pumps in Mining Operations
These submersible pumps in mining applications are installed for controlling pit and shaft water levels, enabling the extraction process to proceed in safety.
As would be expected from such a critical function within mining, they are designed to handle high volumes of water without suffering any loss of efficiency.
They are solidly built and can operate efficiently in unfriendly conditions.
Challenges and Solutions in Dewatering Processes
In this regard, appropriate selection of the pump to specific conditions and regular maintenance checks will go a long way in addressing these challenges.
Sophisticated filtration systems fitted at the front end can also be employed on submersible pumps to ensure sustained operation.

Treatment and Disposal of Effluents
Role of Submersible Pumps in Effluent Treatment
Their capability for handling various types of fluid makes them appropriate for diverse stages of the treatment process, thus ensuring that wastewater is treated with efficiency and effectiveness.
Technologies Used with Submersible Pumps
These pumps very often operate in concert with other sophisticated technologies, filtration systems, and biological treatment processes.
In this respect, integration enhances the overall effectiveness of the wastewater treatment facilities to efficiently remove the pollutants and meet environmental regulations.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
Effluent management has to be treated in accordance with set environmental regulations.
Submersible pumps help such facilities meet the set standards for the effective processing and disposal of wastewater.
Understanding the regulatory demands sets a roadmap for operators to avoid punishments that might question the viability of their operations.

Advantages of Submersible Pumps
Energy Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
One of the major advantages of submersible pumps is their energy efficiency.
Operating underwater, the submersible pumps can supply the base fluid with much lower power consumption compared to surface pumps.
Lower operating costs come directly from the efficiency and, therefore, are economically viable for municipalities and industries.
Space-Saving Design and Installation Flexibility
The design of submersible pumps is compact and can therefore be installed in very tight spaces with no need for an extended structure.
This flexibility allows the pumps to also be convenient in urban environments where space is limited.
Their installations can be done in various ways to suit multiple purposes, making them more flexible.
Less Maintenance
Relatively speaking, submersible pumps are less maintenance-heavy compared to conventional pumps.
Due to their operation while submerged, they are not as exposed to the natural environment and, therefore, tend to have fewer wear-and-tear problems.
The need to conduct periodic maintenance checks is still there; however, this particular burden is greatly reduced.

Challenges and Considerations
Possible Problems in Operating a Submersible Pump
Balancing the very high reliability of submersible pumps are operational problems unique to submersibles, including clogging and/or overheating.
Such may be due to sediment in the fluid or improper installation.
These are some of the areas of concern that operators should be aware of to facilitate problem-free operation.
Operational Requirements
The selection of a proper submersible pump is done based on various factors, such as the type of fluid handled, flow rates, and depth of installation.
All these considerations during selection are extremely important so as to offer superior performance and evade operational problems.
Importance of Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
By putting in place a scheduled preventive maintenance program, the majority of the problems can be observed ahead of time, thereby reducing the frequency of shutdowns and lowering repair costs.
The result of this will be the efficiency of the pumps through their lifetime.

Conclusion
In short, submersible industrial pumps are indispensable parts of any water and wastewater treatment system.
Their excellent performance in transporting fluids contributes to public health, protection of the environment, and effectiveness overall.
As more demands rise with regards to practical solutions in water management, so will dependence on pumping technologies that can perform reliably.
Submersible pumps represent a forward-thinking approach to water scarcity and challenges concerning wastewater, thus becoming crucial in sustainable practices.
The investment in this technology pays off not only in better management of water and wastewater but also in terms of long-term sustainability and operational efficiency.

