Improvement in their performance is highly essential for both efficiency and operating life prolongation.
In understanding how such pumps can have their performance enhanced, customers will save on costs and obtain reliable operation.
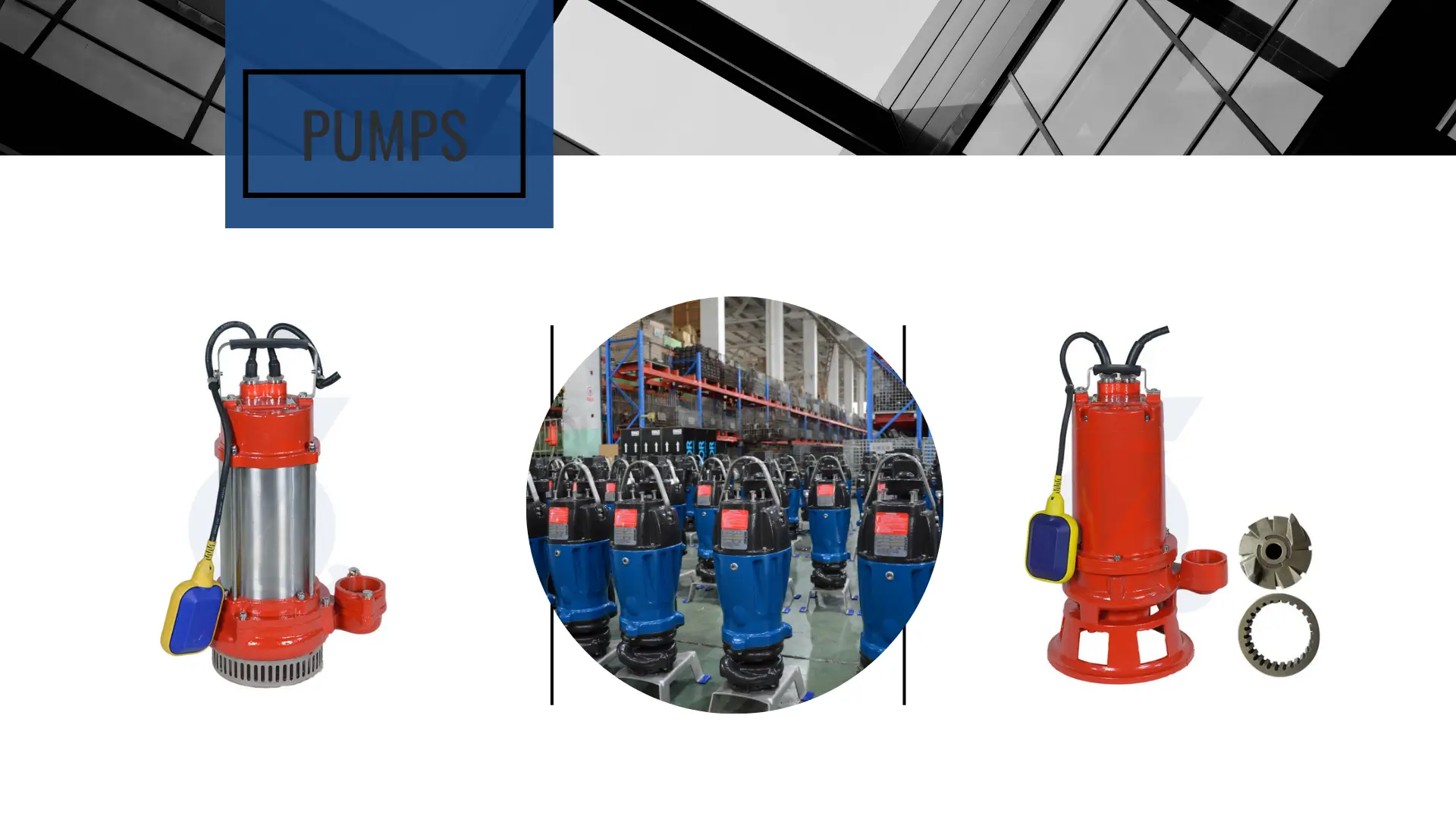
Understanding Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps are special mechanisms that can operate underwater.
Hence, they become very effective in those applications which require the transportation of fluids either from lower to higher elevations or from a submerged position.
Design and Structure
1. Compact Design
Submersible pumps are normally compact and streamlined to fit in small places. In that respect, it allows operation in wells, basements, and other confined areas with efficiency.
2. Main Components
The motor is normally hermetically sealed to avoid water and contaminants. It provides the power necessary for driving the impeller of the pump.
The impeller is the rotating member which transfers the fluid.
Factors Affecting Pump Performance

Pump Size and Capacity
1. Importance of Correct Sizing
Proper sizing and capacity selection for the submersible pump are called for because efficiency can only be guaranteed if the actual process requirement is matched with the appropriately sized equipment.
A wrongly sized, larger pump will lead to wastage of excessive energy and thus operational costs; a pump of inappropriate, smaller size will work without stop at full capacity and overheat into a mechanical failure.
2. Flow Rate Requirements
The amount of fluid to be transferred, combined with the rate it will need to be pumped, can be quantified.
In this manner, peak demand versus average consumption can be weighed to determine the correct pump size.
3. Pressure Head
Normally, to choose the right kind of pump to provide the desired pressure without excessive strain, one needs to calculate both the vertical-lift requirements and any friction losses in the piping system.
Characteristics of Fluids
1. Viscosity
The viscosity of the fluid to be pumped is one of the direct factors in the deliverability in a system.
Thicker fluids are difficult to pump and may demand a more robustly designed pump.
Examples are viscous liquid pumping, such as sludge or oils; these might require a larger impeller on the pump.
2. Temperature
The temperature of a fluid affects the selection of the pump materials and performance.
While higher temperatures lower the viscosity of some fluids, it may degrade certain materials.
Ensure the pump is rated for the temperature range of the fluid for long-term reliability.
3. Chemical Composition
It is the basis of material selection to be used which will withstand the corrosion or deterioration processes.
Indeed, pumps used to handle aggressive chemicals have to be made from materials that are resistant to such fluids; otherwise, they will fail in service.
Installation Conditions

1. Alignment and Location
Setting up the pump correctly in place with the piping that is used to discharge reduces abrasion on the parts of the machine.
This can be a problem for the machine because incorrect adjustment of position causes extra vibration, which leads to a shorter operational life for a pump.
2. Depth and Submersion Level
A very deep installation of the pump may involve more energy to operate, while a very high installation may not work effectively.
The manufacturer’s recommendation regarding submersion levels for best performance should be followed.
3. Site Conditions
Methods of installation will also be influenced by environmental considerations, such as water conditions-suspended material, silt, etc.-and temperature changes.
Accurate site analysis can help in the development of appropriate installation techniques with a view to enhancing operational efficiency and the life of pumps.
Tips for Optimizing Performance
Regular Maintenance
1. Routine Inspections
Closely monitoring the pump and the components may reveal a looming problem that can be addressed before it actually occurs.
It would also include examination of motor, impeller, and seals for wear and tear or damages.
2. Lubrication
Friction and wear cause early failures when moving parts are not lubricated well.
The manufacturer’s instructions on what and how frequently to lubricate should be followed in order to assure the best results.
3. Seal Inspection
Regular checking and replacing of seals when necessary will prevent damage and reduce costly downtime.
Read More:
- The Advantages of Submersible Pumps Manufacturer in China
- Evaluating the Quality of Submersible Pumps from China
- Types of Submersible Pumps Available in China
Monitoring and Adjusting Pump Speed
1. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
Installation of VFDs enables pumps to make real-time adjustments to the speed depending on demand.
This feature is very effective in applications with flow rate variations, since the pump does not work more than required.
2. Energy Economy
With the variation in the pump speed, the energy consumption can be drastically economized.
Running at lower speeds during non-peak periods can mean substantial savings in energy costs and prolong wear and tear on the pump.
3. Optimization of Performance
Monitoring flow rates and pressure will again provide useful information in adjusting the operating setup of the pump.
This information can be analyzed using data analytics in following performance metrics over time; hence, making sure informed adjustments to keep the pump running at ultimate efficiency is achieved.
Using the Right Accessories
1. Filters and Strainers
Filters can be installed to stop debris entry into the pump, which saves critical components while increasing the overall efficiency.
2. Check Valves
Check valves inhibit reverse flow, enabling the fluid to flow in one direction.
This improves efficiency and furthermore stops damage of the pump due to backflow.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
1. Understand Energy Consumption
Submersible pumps can be quite energy-intensive. Knowing the energy requirements of your pump and how it will operate will assist in keeping your costs down.
2. Selecting Energy-Efficient Models
When purchasing new pumps, make sure that you select energy-efficient models that meet or even exceed certain industrial standards.
Such types of pumps operate with lower power consumption without sacrificing their output.
3. Energy-Saving Practices
Accordingly, good energy management can be realized when operational practices are reviewed regularly and patterns that lend themselves to improvement are identified.
A very straightforward modification involves scheduling the operation of a pump during off-peak hours in order to reduce energy costs.
Conclusion
Performance of all the submersible pumps should be enhanced for every buyer.
Any person will be assured of the pump’s efficiency and reliability through understanding its factors that affect performance, coupled with following the best practices.
If you have any other question or need personal advice on the best choice of a submersible pump, do not hesitate to contact us for consultation.

