Selecting the right pumps for super-large waterworks is a critical decision that impacts efficiency, reliability, and overall project success.
The scale and complexity of such projects necessitate careful consideration of various factors to ensure that the chosen pumps meet operational demands while also being cost-effective.
This guide explores key considerations to keep in mind when selecting pumps for large-scale waterworks, providing valuable insights for decision-makers to make informed choices that will enhance the efficiency and longevity of their systems.
What Are the Key Factors in Pump Selection?
Flow Rate Requirements
The flow rate is a fundamental parameter in pump selection, representing the volume of water that needs to be moved within a specific timeframe, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s).
Accurately determining the required flow rate is imperative to ensure the pump can maintain operational efficiency and meet the demands of the system.
Inadequate flow rates can lead to insufficient water supply, while excessive flow can result in wasted energy and increased wear on the system.
Head Requirements
Head is another critical factor in pump selection, referring to the height that the pump must lift water from its source to its discharge point.
Understanding the total dynamic head (TDH) is essential, as it includes not only the vertical lift but also the friction losses encountered in the piping system.
A pump must be capable of overcoming these head requirements to operate effectively.
Calculating the TDH accurately ensures that the selected pump can deliver the necessary pressure and flow to meet system demands.
Pump Efficiency
Efficiency is a vital consideration in the selection of pumps, especially for large waterworks where energy costs can be substantial.
More efficient pumps consume less power while delivering the same flow rate, resulting in lower operational costs over time.
Understanding the pump’s efficiency curves allows for better comparisons between different models, helping to choose a pump that maximizes energy utilization.
High-efficiency pumps contribute to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with sustainability goals.
How Does the Type of Fluid Affect Pump Selection?
Characteristics of Water
While water is the most common fluid in large waterworks, its characteristics can vary significantly based on factors such as temperature, turbidity, and the presence of particulates.
These variations can impact pump performance, prompting the need for pumps that can handle specific water conditions.
For example, water with high levels of sediment may require pumps with enhanced filtration capabilities to prevent clogging and ensure smooth operation.
Chemical Composition
In some cases, the water being pumped may contain chemicals or contaminants that require special consideration.
For instance, water sourced from industrial processes may have varying chemical compositions that can corrode standard pump materials.
Selecting pumps made from materials resistant to chemical degradation is essential to maintain reliability and longevity in such environments.
This ensures that the pump can operate without the risk of failure due to material incompatibility.
Temperature and Pressure Considerations
Pumps that operate under high-temperature or high-pressure conditions require specific designs to ensure reliability and safety.
Standard pumps may not withstand extreme conditions, leading to potential failures.
Therefore, it is crucial to evaluate the operational environment and select pumps engineered to handle the anticipated temperature and pressure ranges.
Specialized pumps can provide the necessary durability and performance, ensuring continuous operation in demanding situations.
How Do Environmental Conditions Impact Pump Selection?
Site Accessibility
The location of the waterworks can significantly influence the type of pump selected.
Pumps must be accessible for installation and maintenance, which may dictate specific designs or configurations.
In remote or challenging environments, selecting pumps that are compact and lightweight can facilitate easier transport and installation.
Accessibility considerations also extend to maintenance, where easy access to components can simplify routine servicing and emergency repairs.

Temperature Extremes
Pumps operating in extreme temperatures must be capable of functioning reliably in such conditions.
Selecting pumps designed to withstand low or high temperatures is crucial to prevent malfunctions.
For example, pumps operating in freezing conditions may require insulation or heating elements to prevent freeze damage, while those in hot environments may need cooling mechanisms.
Assessing the temperature range of the operational environment is essential for ensuring that the selected pumps perform optimally.
Seismic and Weather Resistance
In areas prone to earthquakes or severe weather, pumps must be designed to withstand these conditions to ensure continued operation.
Seismic-resistant pumps feature reinforced structures and anchoring systems that help prevent damage during seismic events.
Additionally, weather-resistant designs protect pumps from rain, snow, and extreme winds, ensuring reliable functionality in adverse conditions.
Evaluating the potential environmental risks associated with the site is critical for making informed pump selection decisions.
Also Read:
- Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Waterworks
- Material Selection for Durable Submersible Pumps in Large-Scale Waterworks
What Role Does Energy Efficiency Play in Pump Selection?
Understanding Energy Consumption
Energy consumption can be a significant portion of operational expenses in large waterworks.
Choosing energy-efficient pumps can lead to substantial savings in utility costs, making them a priority in pump selection.
Efficient pumps minimize energy usage while still delivering the required performance, contributing to lower long-term operational costs.
Understanding the energy profiles of different pump options can help in selecting models that align with budgetary goals without sacrificing performance.

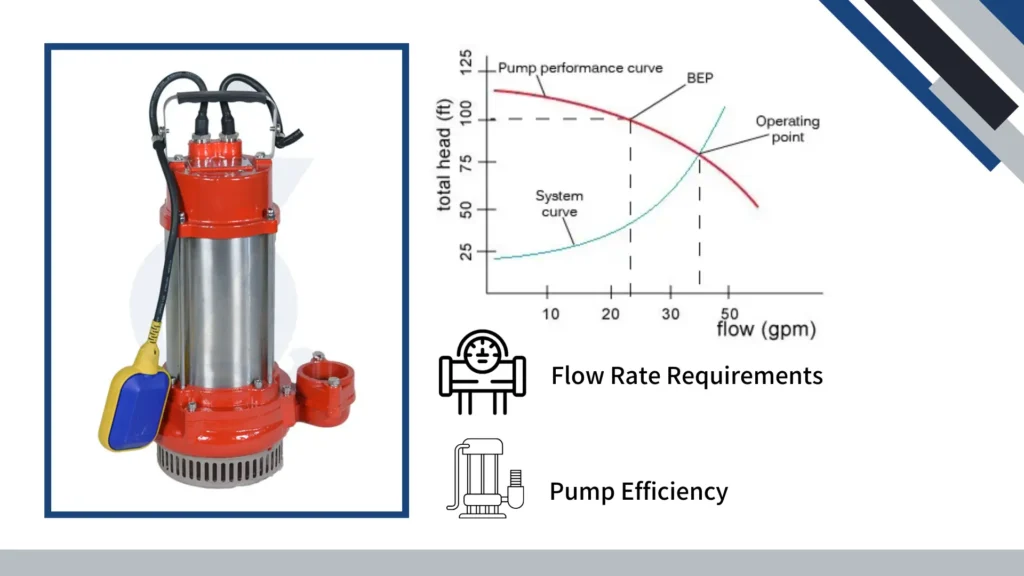
Evaluating Pump Performance Curves
Analyzing performance curves is essential for assessing how well a pump will operate under varying conditions.
Performance curves depict the relationship between flow rate, head, and efficiency, enabling users to understand how the pump will perform in real-world scenarios.
Evaluating these curves helps in selecting pumps that optimize energy use and meet specific operational requirements.
This analysis is critical for ensuring that the selected pump will perform effectively across a range of expected conditions.
Long-Term Cost Savings
Investing in energy-efficient pumps may entail a higher upfront cost; however, it can result in lower operating costs over the life of the pump.
By reducing energy consumption, these pumps can recover their initial investment through savings on utility bills.
Additionally, lower energy use contributes to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with sustainability objectives.
Evaluating the long-term cost benefits of energy-efficient pumps is essential for making informed investment decisions.
How Do Regulations and Standards Affect Pump Selection?
Compliance with Local Regulations
Understanding local regulations related to waterworks is essential for ensuring compliance and safety.
Pumps must meet specific standards to operate legally and effectively in their intended applications.
Familiarizing yourself with local codes and regulations helps avoid potential legal issues and ensures that the selected pumps are suitable for the intended use.

Industry Standards
Familiarity with industry standards is crucial for ensuring that the selected pumps are reliable and effective.
Various organizations set standards for pump performance, safety, and efficiency, guiding manufacturers in producing quality products.
Adhering to these standards ensures that the pumps meet established benchmarks for performance and reliability, ultimately contributing to the success of the waterworks project.
Environmental Impact Considerations
Choosing pumps that minimize environmental impact is increasingly important in today’s regulatory climate.
This includes evaluating energy use, emissions, and the potential for spills or leaks.
Selecting pumps designed with environmental sustainability in mind can enhance the overall ecological footprint of the project, aligning with broader goals of environmental stewardship and compliance with regulatory frameworks.
What Are the Benefits of Advanced Pump Technologies?
Smart Pumping Solutions
Modern pumps often come equipped with smart technologies that allow for real-time monitoring and control.
These technologies can enhance efficiency and performance by providing data on operational conditions, enabling proactive adjustments to optimize performance.
Smart pumping solutions facilitate better management of water resources, contributing to improved overall system efficiency.
Integration with Automation Systems
Integrating pumps with automation and control systems can enhance operational efficiency and reduce the need for manual intervention.
Automated systems can monitor pump performance, detect anomalies, and adjust operations based on real-time data, ensuring optimal functionality.
This integration can lead to improved reliability and reduced labor costs, as automated systems handle routine monitoring and adjustments.

Predictive Maintenance Capabilities
Advanced pumps can provide data that enables predictive maintenance, helping to identify potential issues before they escalate into significant problems.
By analyzing performance data, operators can schedule maintenance activities based on actual pump conditions rather than relying on fixed schedules.
This approach minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of the pumping systems, ensuring continued reliability and performance.
How Do Cost and Budget Considerations Affect Pump Selection?
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Costs
While it may be tempting to choose the cheapest option available, it is essential to consider both initial investment and long-term operational costs.
Lower-priced pumps may not offer the same level of efficiency or durability, leading to higher maintenance costs and energy consumption over time.
Evaluating the total cost of ownership helps in making informed decisions that align with financial goals while ensuring reliable performance.
Life Cycle Cost Analysis
Performing a life cycle cost analysis allows decision-makers to evaluate the total cost of ownership for different pump options.
This analysis considers initial costs, maintenance expenses, energy consumption, and expected lifespan, providing a comprehensive view of the financial implications of each option.
By understanding the long-term costs associated with various pumps, project managers can make more informed selections that balance performance with budget constraints.
Budget Constraints
Understanding budget limitations is crucial when selecting pumps for super-large waterworks.
Finding a balance between quality and cost is essential to ensure that the selected pumps meet both performance and financial expectations.
Engaging with manufacturers and suppliers can provide insights into cost-effective options that still deliver the required performance, facilitating better budget management.

Conclusion
Selecting pumps for super-large waterworks involves careful consideration of various factors, including flow rate, head requirements, material durability, and energy efficiency.
By taking into account the unique challenges presented by large-scale projects, decision-makers can choose pumps that not only meet operational needs but also provide long-term value.
With the right information and understanding, the selection process can lead to successful outcomes in waterworks projects, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and sustainability for years to come.
Investing time in this process will ultimately pay off in the form of enhanced performance and reduced operational costs, making it a vital aspect of project planning and execution.

