Pumping systems would comprise the most important lifelines of a municipal pipe dream in terms of water distribution and sewage disposal.
These play their role in effectively transporting the clean drinking water supply to domestic and commercial outlets while relieving sewage and stormwater drainage.
Public health and safety will considerably be compromised without reliable pumping systems because it will not only lead to water shortages but also to contamination.
Increasing energy prices and environmental concerns have brought the efficiency of pumping systems to the forefront of municipal agendas.
Practically substituting less efficient pumps with energy-efficient models can bring down the total cost of operations and emissions strikingly at national municipal levels.
Water-saving practices through sustainable selection and management also contribute to the long run of resource conservation and environmental stewardship.
Types of Pumps Commonly Used in Municipal Applications
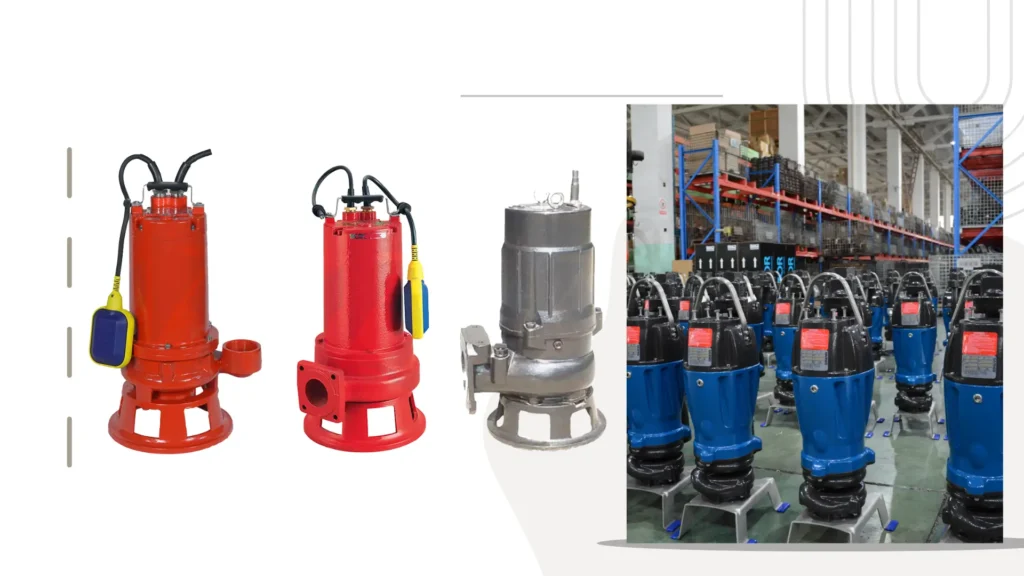

Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are employed widely for municipal applications owing to their very good performance in pumping large volumes of water efficiently.
Instead of using the suction and discharge ports to draw water into the pump through its peripheral impeller, a centrifugal pump takes kinetic energy in the fluid and converts the rotational energy from the motor to kinetic energy in the fluid propelling it toward the outlet of the pump.
The simple but highly efficient design makes this pump perfect for use in water supply systems and irrigation.
Positive Displacement Pump
Positive Displacement Pumps trap a limited volume of fluid in a chamber and then force it through the discharge pipe.
This type of pump generally provides much higher efficiency when developed and applied to lubricating and flux-impeding liquids, such as sludges or slurries.
With this kind of flow control provided, it also becomes very useful in processes such as chemical dosing at wastewater treatment facilities.
Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps work completely submerged, making them excellent in areas of sewerage & drainage work.
They pull water from deep underground or from surfaces that are flooded.
Their compact structure saves space, and thus, infrastructure is reduced, making it cost-effective for municipalities.
Diaphragm Pumps
Diaphragm pumps are known to easily handle corrosive or viscous liquids with functionality involving flexibility in diaphragm for creating a small vacuum to draw in fluids and push them out.
Thus, they are also qualified for various municipal functions such as chemical handling and wastewater treatment, where precise flow control is essential.
Factors Influencing Pump Selection
Flow Rate Requirements
Knowing the required flow rate is a fundamental consideration of pump sizing.
Each municipal application carries specific flow demands that determine size and capacity.
True flow rate calculations: such that pumps can be chosen not to waste energy or resources when meeting current needs while remaining capable of fulfilling future needs in the event of extension or peak demand/ unforeseen circumstances.
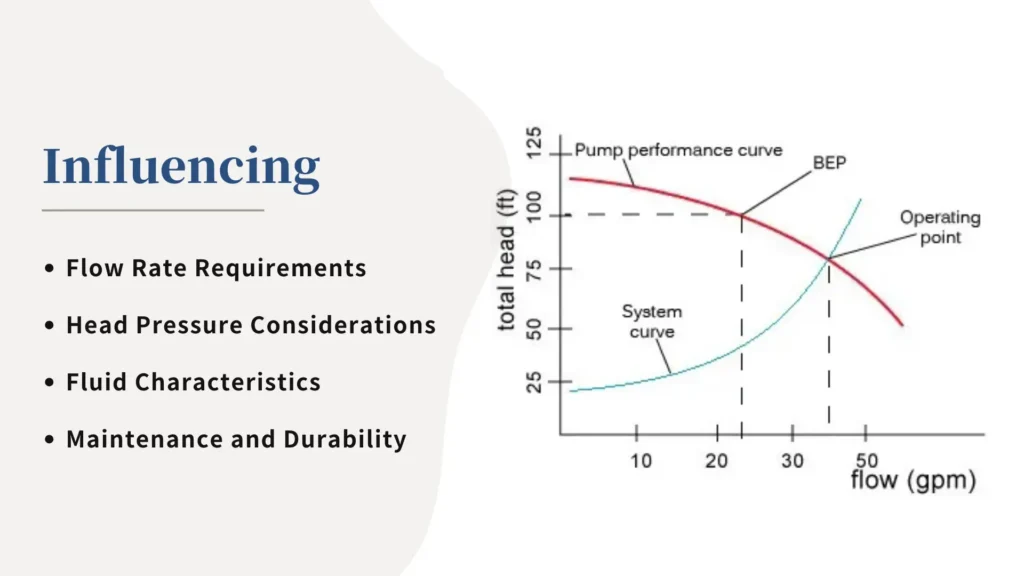
Head Pressure Considerations
Head Pressure, namely that height to which the pump must lift or both pump and water source need some more uplift, lifts water.
Varying types of pump perform well with a different head pressure, so knowing this requirement would help municipalities to select pumps which operate more energy-efficiently and more reliably in their specific environment.
Fluid Characteristics
The properties of the liquid being pumped, like its viscosity and temperature, toxicity, and corrosiveness, have a strong effect on the choice of pump.
A corrosive liquid, for instance, needs to be pumped into special materials to avoid corrosion, while liquids with a high viscosity often must be pumped by means of positive displacement pumps.
Maintenance and Durability
Health considerations and considering the lifetime of pumps are a priority for a municipality to cut downtime and repair costs.
Pumps that require less maintenance or operate longer are highly cost-effective and enhance reliable service delivery to the municipality.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Pump Type
Centrifugal Pumps
Advantages
Centrifugal pumps move massive quantities of water and operate at high efficiency. The design of this pump is simple, making it easy to maintain and cost-effective to operate.
Disadvantages
The aforementioned characteristics of centrifugal pumps deteriorate when high-viscosity liquids and high pressures necessitate pumps.
Positive-Displacement Pumps
Advantages
They are further qualified in producing some sort of a constant output at the pump discharge around changing pressures, so well suited to the very precise applications of measurement.
They can also perform very well during the pumping of thick fluids.
Disadvantages
They have a very complicated design so that maintenance costs will also be higher, and it needs frequent service compared to centrifugal pumps.
Submersible Pumps
Advantages
They are quite efficient for submerged applications and save space because of compactness, and they eliminate the need for additional infrastructure, such as pump stations.
For all practical purposes, they are designed to fulfill the efficiency requirement directly within an application.
Disadvantages
One such downside is the risk of overheating, if not properly monitored; and they are much more complicated to service due to the underwater location.
Diaphragm Pumps
Advantages
They can also be used with highly corrosive media and very viscous fluids, which makes them suitable for very fluid applications.
They offer excellent flow control and are therefore suitable for sensitive environments.
Disadvantages
Nevertheless, they do not have as high flow rates as many other types of pumps, and some might even be more expensive in the beginning.
And More:
The Advantages of Submersible Pumps Manufacturer in China
Cost Considerations
Short-term Cost against Long-term Savings
Municipalities need to consider an initial investmentrequisite to install a pump compared to long-term savings because, although some pumps are expensive at their initial purchase, their efficient and reliable performance saves much in energy and maintenance costs.
Like that, a thorough cost benefits analysis is needed to make informed decisions.
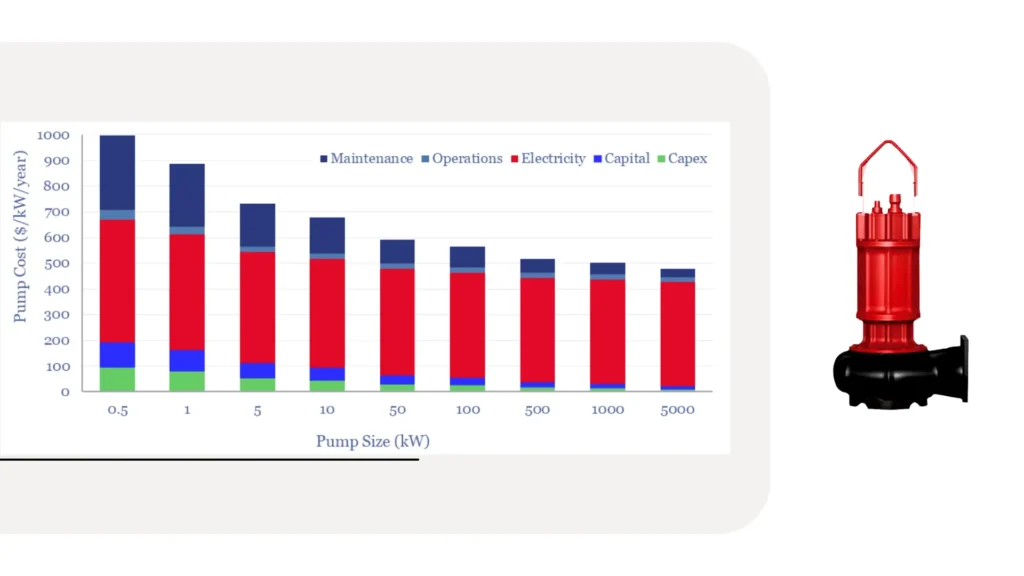
Energy Consumption and Efficiency Rating
Hugely, energy-efficient pumps can significantly reduce operating costs and, therefore, environmental emission.
In this context also, municipalities should opt for energy-efficient pumps, that is, impart those installed with high efficiency rating, which will substantially depend upon energy consumption and, ultimately, bills for electricity.
Maintenance Costs
It is necessary to understand the demand and cost for maintaining different pump types to ensure effective budgeting.
For once, they can choose pumps that need less frequent maintenance or simpler service to save on costs that municipalities would not have budgeted for.
Also Read:
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Submersible Pumps in Municipal Systems
Energy Efficiency Programs
Incentives for Municipalities
Various governments and organizations have incentives for municipalities adopting energy-efficient pumps.
The types of these programs are grants, rebates, or tax credits that help answer the high initial expenses for buying and installing high-efficiency pumping systems.
Evaluating Energy Performance
Regular energy performance evaluations of the different pumping systems should be done in a municipality.
An energy audit can reveal inefficiencies and improvements, incomplete recommendations on improvements that should be undertaken or equipment that will be replaced for maximum energy savings.
Long-Term Environmental Benefits
Energy-efficient pumps result in lower operational costs and will, therefore, have long-lasting environmental benefits.
Since energy consumption is reduced, the emissions of greenhouse gases are minimized and are therefore consistent with sustainability goals, which are also part of the commitment of the municipality to act as an environment steward.

Training and Workforce Development
Importance of Skilled Personnel
Much depends on skill in operation and maintenance of municipal pumps.
To have expertise on the full range of current knowledge and skills essential for effective management of pump systems, an organization should consider investing in training programs.
Continuous Education and Certification
Consider implementing continuous education and certification programs for the employees.
It keeps the personnel being updated with the latest technologies and best practices in pump operation and maintenance, thus making the whole system more reliable.
Creating a Repository
Establishing a centralized repository or resource center can help facilitate the sharing of information among municipal workers and may include, but not limited to, manuals, troubleshooting guides, and case studies, collectively giving access to valuable information that will empower staff in handling challenges related to pump systems.

Conclusion
It is important for municipalities to understand the varying types of pumps and their specific applications if they are to optimize their water management systems.
Each of these pump types has its unique advantages and disadvantages, which should be taken into consideration in relation to specific needs.
A city must not adopt a selective approach to pump selection where it evaluates the flow requirements, head pressure, fluid characteristics, and long run costs.
Therefore, the decisions made can, with precision, be broadened to better grounds: better infrastructure, improved services delivery: all in the general betterment of society.

